How Drone Technology Can Help Improve Farming System
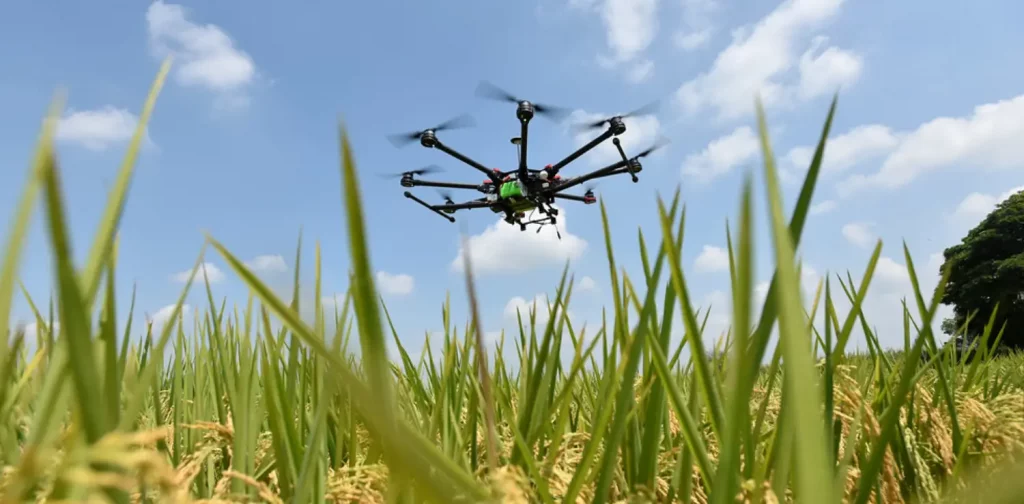

Photo by Neil Palmer on Flickr
People around the world, especially those living in rural areas, heavily rely on farming as their main source of income. Agriculture has also become an important key to meeting food demand globally. Unfortunately, farming systems are experiencing a number of challenges globally, including a non-optimal supply of water, soil degradation, shortage of fertilizers and insecticides, and the lack of labor.
Importance of Farming in Countries
Agricultural activities, including farming, are vital to improve the food security and strengthen the economy of many countries. One of them is Vietnam. As the world’s third-largest rice exporter, rice farming plays a vital role in Vietnam’s economy with most rice produced in the Mekong River Delta (MRD), the rice bowl of Vietnam.
Similarly, farming is a significant economic sector in India and African countries. It contributes about 17% to the total GDP (gross domestic product) and employs more than 60% of the workforce in India. For several African countries, farming holds significant importance in their economies, with smallholder farmers constituting approximately 23% of the region’s GDP.
Application of Drone Technology
Drones are robotic technology that contributes to improved efficiency and reduced costs in various industries, including farming. Applying advanced technology such as drones can help optimize agricultural production.
This technology has several advantages. In Vietnam, drones can help supply water, fertilizer, and insecticides with optimal concentrations so as to support the growth of agricultural crops. Combined with alternate wetting and drying (AWD), the use of drones also can minimize methane gas emissions.
In India, drones are also applied by the farmers. Kumar, a farmer from Bihar, India, said, “Drone technology has played a significant role in the positive change. It can cover the same area in eight or nine minutes, whereas it used to take a worker seven or eight hours to spray an acre of land.”
In the past, Kumar found it difficult to find workers quickly when disease struck his field. Should he manage to locate them, the illness would have already ravaged his crops by the time they completed applying pesticides. But with drones, he can handle the issue.
Meanwhile, in Africa, drones are used to enhance soil quality and monitor pests and diseases. For example, in Nigeria, drones equipped with light spectrometers are used to map and analyze soil, aiding farmers in optimizing crop yields by assessing nutrient levels and moisture content. In Kenya, drones with thermal cameras are used to detect pests and diseases in crops, and in South Africa, they are used to monitor livestock health and location.
National Framework Needed
Drone technology helps farmers increase crop productivity by saving water, being much faster at applying chemicals, and being used for a variety of agricultural tasks, which can benefit a country’s economy.
However, national frameworks must be established and enforced to guarantee responsible and safe use of drones. Some studies suggest that drone usage could also bring negative impacts on humans and the environment, particularly wildlife. Thus, further research and improved regulations are crucial to maximize the advantages and lessen the risks of drone technology in farming systems.
Editor: Nazala Kusuma

Co-create positive impact for people and the planet.
Amidst today’s increasingly complex global challenges, equipping yourself, team, and communities with interdisciplinary and cross-sectoral insights on sustainability-related issues and sustainable development is no longer optional — it is a strategic necessity to stay ahead and stay relevant.


 The Widespread Impacts of Severe Drought in Somalia
The Widespread Impacts of Severe Drought in Somalia  Ensuring Access to Justice for Women and Girls
Ensuring Access to Justice for Women and Girls  The Invisible Infrastructure: What ASEAN’s Carbon Market Needs Most
The Invisible Infrastructure: What ASEAN’s Carbon Market Needs Most  Indonesia Ruled to Recognize Chronic Illness as a Disability
Indonesia Ruled to Recognize Chronic Illness as a Disability  Clean Cooking as a Developmental Multiplier in Africa
Clean Cooking as a Developmental Multiplier in Africa  Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon
Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon