Early Detection System for Wildfire Preparedness Using Phones
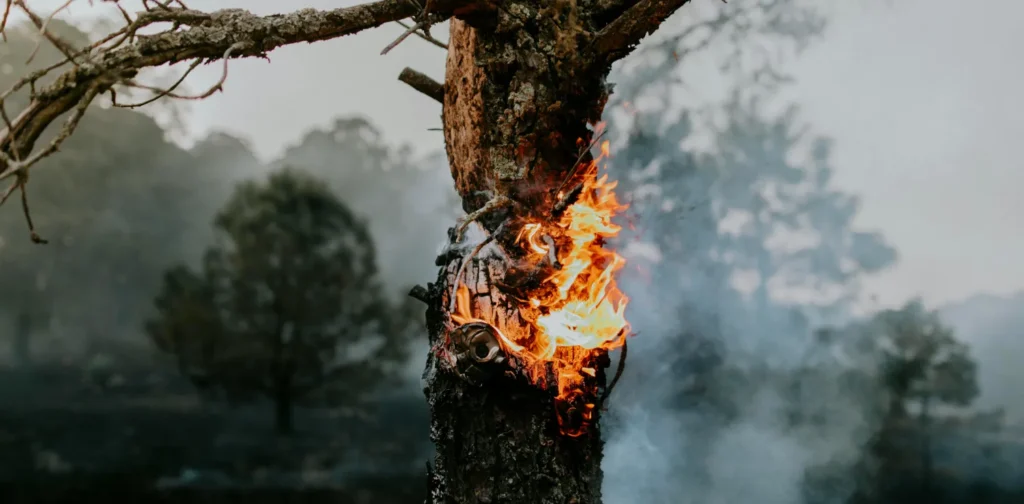

Photo by José Luis Photographer on Pexels
The rising temperatures associated with climate change are intensifying the risk of natural disasters, particularly wildfires. Therefore, it is crucial for areas prone to wildfires to develop risk reduction and mitigation strategies. A study from the University of Southern California has introduced a new system that maps wildfires more efficiently using phones to improve wildfire preparedness.
Climate Change and Wildfire Loop
A study from the World Meteorological Organization explains how climate change, air pollution, and wildfires are linked in a harmful feedback loop. Climate change increases the risk of wildfires, which in turn create air pollution. The emissions from wildfires, along with other greenhouse gasses, contribute to global warming, causing the cycle to repeat.
Wildfires severely impact people’s lives and harm the surrounding biodiversity. Studies have shown that climate change has already caused wildfires to last longer, happen more often, and cover larger areas.
This year alone, wildfires have already burned more than a million acres of land in California. Similarly, Chile experienced wildfires that caused hundreds of casualties early in the year, and Brazil faced a series of devastating wildfires, burning more than 20 million acres of landmass.
The UN Environment Programme (UNEP) predicts that extreme wildfires will become more common and intense worldwide, with the most extreme fires increasing by as much as 50% by 2100.
New Method on Mapping Wildfire
Despite the importance of wildfire preparedness, tracking and mapping processes for early detection can be challenging. Traditional methods, such as satellites, drones, and lookouts, often have high costs, slow response times, and limited coverage. These drawbacks mean firefighters have to rely on human observation.
A recent study from the University of Southern California developed a new method that could significantly reduce mapping time. The system uses low-cost mobile phones with cameras and sensors placed in high-risk areas. Once in place, the phone detects signs of fire from nearby vegetation, even identifying a fire before it fully appears.
By utilizing computer vision and multi-modal analysis, the system can detect wildfires from up to 3,000 feet (roughly 900 meters) away and map them to within 180 feet (55 meters) of their origin. The system has shown accuracy in mapping and locating fires quickly during simulations. Furthermore, the setup is affordable, costing less than $100, making it accessible to many communities, especially those frequently affected by wildfires.
Improving Wildfire Preparedness and Early Detection
Disasters are unpredictable, and our survival hinges on our ability to prepare for them and detect early warning signs. In the middle of climate change and an escalating risk of human-induced disasters, wildfire preparedness and early detection must be prioritized. Governments must invest in robust disaster preparedness infrastructure, including early detection technologies, to enable timely and informed decision-making. Innovation and technology are essential for creating effective response strategies. Adopting advanced solutions can reduce casualties, vulnerable ecosystems can be protected from disruption, and the well-being of all can be safeguarded.
Editor: Nazalea Kusuma & Kresentia Madina
Dinda Rahmania
Dinda is an Assistant of International Partnerships at Green Network Asia. She holds a bachelor’s degree in International Relations from President University. As part of the GNA In-House Team, she supports the organization’s partnerships with international organizations, governments, businesses, and civil society worldwide through digital publications, events, capacity building, and research.


 The Widespread Impacts of Severe Drought in Somalia
The Widespread Impacts of Severe Drought in Somalia  Ensuring Access to Justice for Women and Girls
Ensuring Access to Justice for Women and Girls  The Invisible Infrastructure: What ASEAN’s Carbon Market Needs Most
The Invisible Infrastructure: What ASEAN’s Carbon Market Needs Most  Indonesia Ruled to Recognize Chronic Illness as a Disability
Indonesia Ruled to Recognize Chronic Illness as a Disability  Clean Cooking as a Developmental Multiplier in Africa
Clean Cooking as a Developmental Multiplier in Africa  Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon
Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon