Open Storage Model for Storing Food Without Electricity
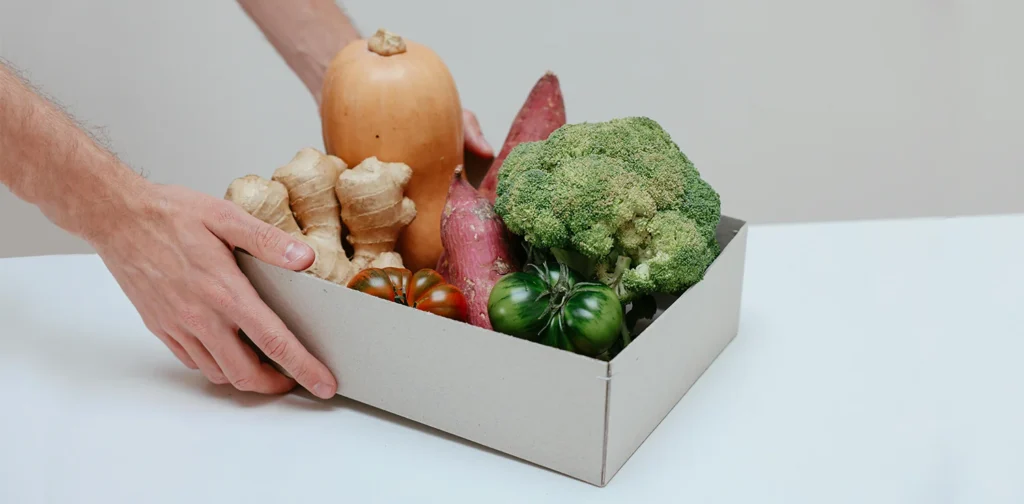

Photo by Cup of Couple on Pexels
Preserving food without electricity may seem challenging without a refrigerator today. However, the climate crisis requires us to be mindful of our electricity consumption, including refrigerator usage. To address this, an open storage model offers a potential solution to store food without electricity.
Cooling Yet Heating
Today, food storage has grown to depend on cooling systems. Refrigerators are among the most common choices for households due to their ability to slow down bacterial growth and help items stay fresh longer, providing a much easier and less time-consuming way to preserve food than traditional methods like pickling, drying, or canning.
Ironically, refrigerators and other cooling systems are heating up the planet due to the intensive energy they consume to maintain consistent temperatures. Since much of the world’s electricity still comes from fossil fuels, this level of energy use has a harmful impact on the environment.
Moreover, coolant gases used by cooling appliances, such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), are extremely detrimental to the environment. Some highly potent HFCs are still being used today, and releasing just one tonne of these gasses has the same environmental impact as emitting 14,800 tonnes of carbon dioxide.
Open Storage Model
Without interventions, excessive use of refrigerators and other cooling systems can accelerate global warming, pushing the Earth closer to surpassing the critical 1.5°C temperature limit. The threshold could be crossed by 2024, with 2023 already the hottest year on record. Therefore, an alternative to conventional cooling food storage systems is needed.
An open storage model could provide a sustainable alternative for food preservation without electricity. The model refers to an open wood container without a lid to maximize airflow and regulate humidity. This prevents excess moisture, therefore reducing the risk of mold and keeping vegetables fresh longer.
Projects like Save Food from the Fridge emphasize the importance of tailoring storage methods to the specific needs of each food item. While refrigerators can be too cold for certain vegetables, the open storage model allows food to be stored in conditions that better suit their natural properties.
For example, root vegetables can be placed in pockets of soil, keeping them fresh for longer. Carrots and scallions can be stored vertically with a sand or soil base to maintain their natural state. Additionally, some open storage designs include a water tray beneath the box to rehydrate vegetables by replacing lost moisture daily.
Another example of this model is La Caja Verde from Argentina, a furniture-based open food storage system. Made from phenolic multi-laminated wood, it is designed to resist moisture and store up to 20 kilograms of food.
Mainstreaming Alternative Food Storage Method
The open storage model shows the possibility of storing food without electricity, reducing environmental harm while maintaining modern convenience. Whenever possible, we can begin shifting to a sustainable lifestyle by rethinking our consumption habits, such as how we store food.
Additionally, supporting systemic interventions, as well as providing funding for practical tools and ideas that can actively reduce our carbon footprint, are crucial steps. Combining innovation, rethinking our daily habits, and mainstreaming good practices is crucial to achieving our climate goals and building a more sustainable future for all.
Editor: Kresentia Madina & Nazalea Kusuma

Co-create positive impact for people and the planet.
Amidst today’s increasingly complex global challenges, equipping yourself, team, and communities with interdisciplinary and cross-sectoral insights on sustainability-related issues and sustainable development is no longer optional — it is a strategic necessity to stay ahead and stay relevant.
Dinda Rahmania
Dinda is an Assistant of International Partnerships at Green Network Asia. She holds a bachelor’s degree in International Relations from President University. As part of the GNA In-House Team, she supports the organization’s partnerships with international organizations, governments, businesses, and civil society worldwide through digital publications, events, capacity building, and research.


 Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon
Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon  From Anxiety to Action: How Youth Climate Activism Is Evolving
From Anxiety to Action: How Youth Climate Activism Is Evolving  India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights
India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights  Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health
Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health  Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year
Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year  Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities
Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities