The Urgency of Wildfire Preparedness Amidst Global Climate Crisis
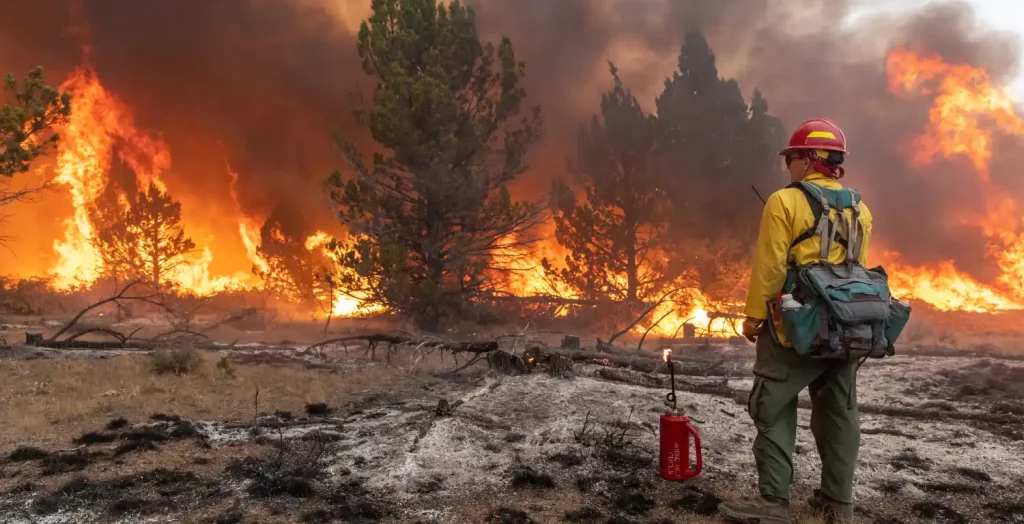

Photo: Neal Herbert on Rawpixel
Disaster preparedness relies on our ability to recognize the subtle signs before they lead to catastrophic events. The challenge is greater in areas that lack effective prevention and early detection efforts. Wildfires are among the recent catastrophes happening around the world as the climate crisis worsens. It underscores the importance of implementing disaster risk reduction, prevention, and mitigation strategies—especially during the dry season. So, what does wildfire preparedness entail?
Wildfire Events and Causes
Wildfires are swift, uncontrollable fires that spread rapidly in areas with vegetation such as forests, grasslands, savannah, and other similar environments. The fire can move quickly and leap across long distances. Its spread is influenced by factors like weather, terrain, and available fuel. The extent of the spread is often determined by wind strength and direction, with dry vegetation serving as its fuel, thus contributing to the expansion of wildfires.
This disaster poses a significant threat to the biodiversity and ecosystems in the area and the population surrounding them. Properties, businesses, land, animals, plants, and human lives could bear the consequences of damages caused by the widespread uncontrolled fire.
In early February 2024, a wildfire erupted along the coast of the Valparaiso region in Chile, resulting in the loss of hundreds of lives and the destruction of thousands of buildings and homes. Additionally, a total of 43,000 hectares of land was affected. While Chile experiences wildfires annually, this year’s event is considered the deadliest due to its number of casualties.
Wildfires can be caused by acts of nature, such as extreme heat waves, lightning strikes, or spontaneous combustion. However, human activities like unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, or arson are also the main causes of wildfires.
For instance, the 2023 Sumatran wildfires in Indonesia were suspected to be caused by land clearing, igniting fire on over three hundred forests and peatlands across the island. The impacts, however, went beyond the island and might have caused transboundary haze in Southeast Asia.
Climate Change as a Deadly Factor to Wildfire
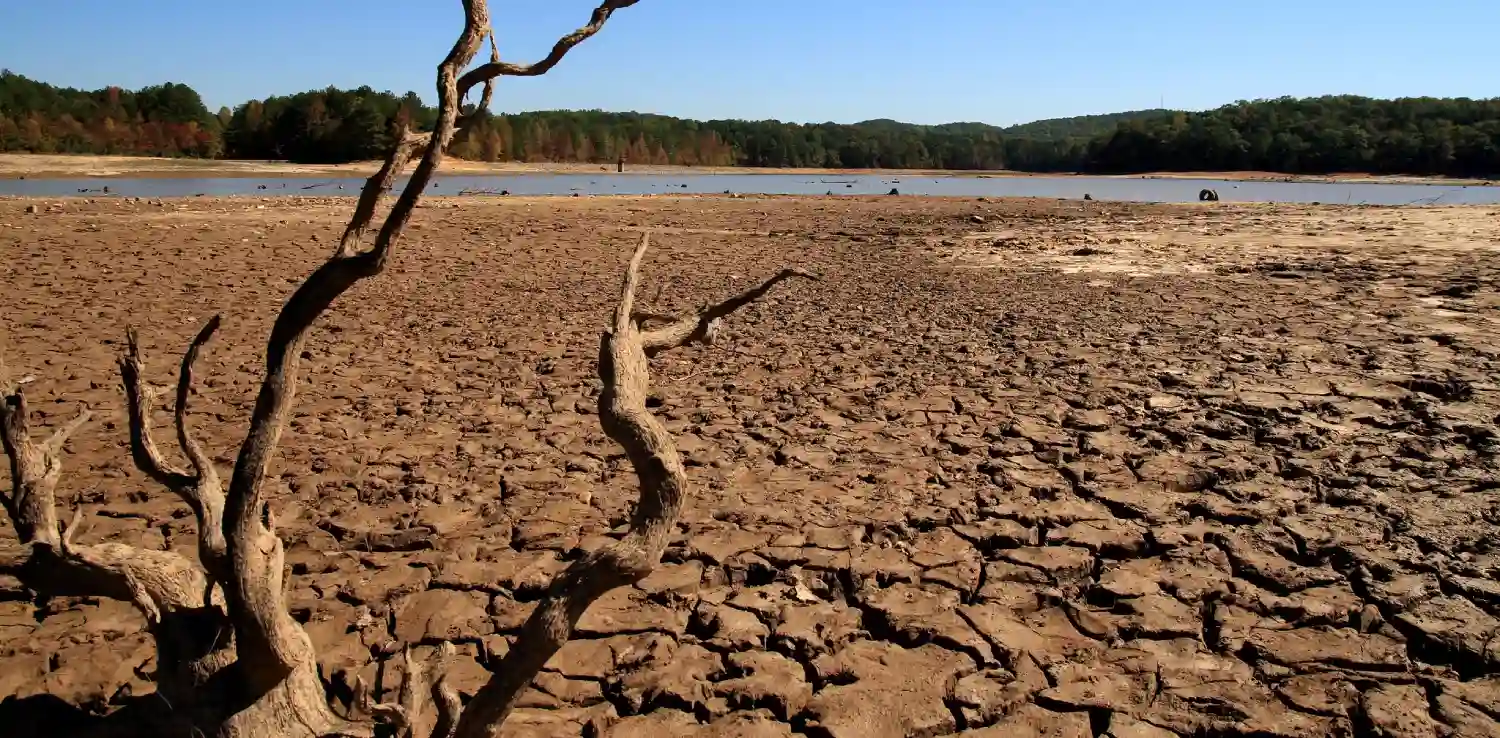

The recent Chilean wildfire underscores how climate change significantly affects wildfires and amplifies their destructive impacts. Scientists attribute the severity of these events to a straightforward factor: the rising temperatures.
A forests expert from the University of Edinburgh School of Geosciences in Scotland, Edward Mitchard, explains that climate change leads to higher temperatures, which cause plants to lose more water through evaporation and soils to become drier. Drier leaves are more flammable, and drier soil means hotter ground that intensifies the heat of the fire and prolongs the fire duration.
Additionally, flash droughts occur more often, affecting surrounding vegetation. A flash drought typically occurs on a seasonal basis, lasts 30-60 days, and could escalate quickly, offering communities and ecosystems in drought-prone regions minimal preparation time. This swift onset can heighten the risks of wildfires and water shortages, emphasizing the critical importance of monitoring and predicting drought conditions.
Wildfire Preparedness
As the planet keeps getting hotter, it is crucial to implement strategies for wildfire prevention and mitigation. From employing technology to taking climate action, here are several points to ensure wildfire preparedness:
- Technology for monitoring and early detection: The use of data analytics, sensors, or video-based fire detection systems helps authorities to swiftly identify emerging threats and prepare measures to mitigate the impact and reduce the risk of widespread damage.
- Water reservoir availability: The reservoirs serve as critical resources in facilitating quick response and strategic deployment of water to extinguish fires, safeguarding both lives and property around the affected area.
- Enforcement of supportive policy: Policy could provide funding that supports mitigation and adaptation of the surrounding vulnerable communities, as well as regulation enforcement around vulnerable areas.
- Encouraging climate action: Implementing measures, such as reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices, helps create a resilient environment less prone to extreme fire events, contributing to the long-term safety and wellbeing of communities, biodiversity, and ecosystems.
Comprehensive wildfire preparedness is vital to safeguard communities, ecosystems, and future generations from the escalating threats posed by the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires fueled by the impacts of a changing climate. Overall, planning and implementing proper prevention and mitigation strategies is possible through a multidisciplinary approach and collective efforts from governments, the private sector, and civil society.
Editor: Nazalea Kusuma


 India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights
India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights  Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health
Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health  Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year
Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year  Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities
Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities  Women in Waste Management: Asia’s Circularity Runs on Women. Its Policies Still Don’t
Women in Waste Management: Asia’s Circularity Runs on Women. Its Policies Still Don’t  Embracing the Business Value of Sustainability
Embracing the Business Value of Sustainability