How Combined Conservation Efforts Help Recover Endangered Iberian Lynx Population
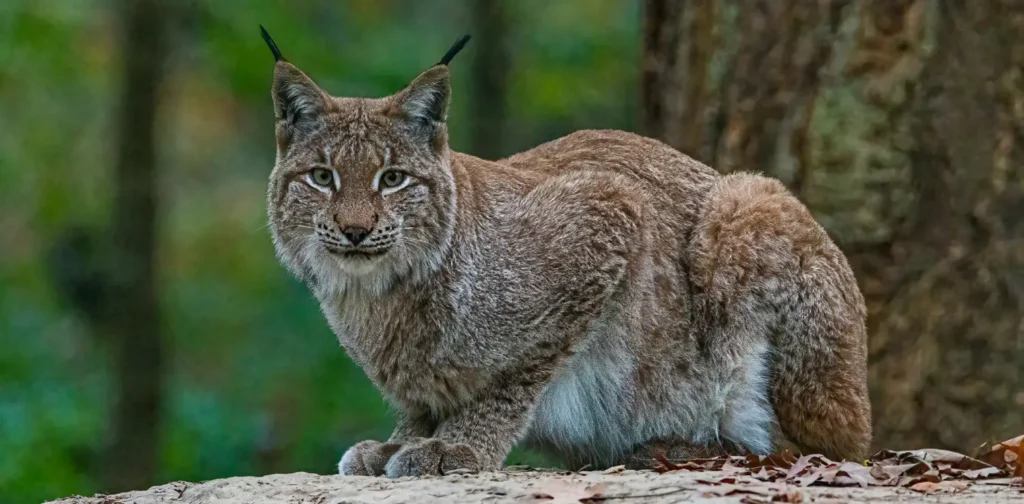

Photo: Kenny Goossen on Unsplash
The Earth’s cycles are influenced by the interrelated roles played by its inhabitants. Ensuring these roles are performed becomes critical, including keeping the role of predators in check. One of them is the currently endangered Iberian Lynx. The bright side is that combined conservation has been shown to help their population gradually recover.
Iberian Lynx for Balanced Ecosystem
The Iberian Lynx is native to the Iberian peninsula and is the keystone species in their habitat. A single lynx can kill as many smaller predators in a year as roughly 20 foxes, which helps small rodents survive. Lynx also tend to stay near larger prey for long periods, causing grazers to avoid their territory which positively affects plant growth.
Despite their important role, a combination of threats has pushed the Iberian Lynx to the brink of extinction. The population hit one of its lowest points in 2001, with just 62 mature individuals remaining, due to hunting, habitat loss, and a declining food supply.
Furthermore, the expansion of infrastructure into their natural habitat poses a significant threat to the species. For example, highways that divide their habitat often result in fatal car accidents.
In 2014, 22 Iberian Lynx were killed in such incidents, which is particularly alarming given the already small size of their population.
Combined Conservation Efforts for Population Recovery
Communities and multiple institutions in Spain have collaborated on various initiatives and partnerships to address the critically low population of the Iberian Lynx. As a result, there has been a positive trend and the population has rebounded significantly over the last two decades. As of today, there are more than 2,000 Iberian Lynxes than twenty years ago.
Among others, the collaboration between the European Nature Trust and CBD-Hábitat has supported the lynx’s population increase. Additionally, local landowners have voluntarily allowed access to their land for conservation efforts. The conservation involves actively monitoring the wild population using camera traps and radio tracking, while nationwide captive breeding programs are continually working to strengthen new wild populations.
Additionally, the conservation efforts utilize nature-based solutions by creating ecological corridors and preserving their natural habitat. This approach creates an environment that not only benefits the Iberian Lynx but also supports other species, including their prey. Equally important step in the conservation is the full protection and restocking of wild rabbits in the natural habitat of the lynx.
Partnership for Wildlife Conservation
Multi-stakeholder partnerships are critical for tackling challenges amid the triple planetary crisis, including endangered wildlife. The Iberian Lynx conservation demonstrates the importance of shared commitment and collaborative actions. Active contributions from governments, scientists, non-governmental organizations, and local communities underline the importance of collective awareness and collaboration for wildlife conservation.
All in all, law enforcement and development that protects the sustainability of the ecosystem must be a key pillar to create a significant and lasting impact on biodiversity protection.
Dinda Rahmania
Dinda is an Assistant of International Partnerships at Green Network Asia. She holds a bachelor’s degree in International Relations from President University. As part of the GNA In-House Team, she supports the organization’s partnerships with international organizations, governments, businesses, and civil society worldwide through digital publications, events, capacity building, and research.


 India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights
India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights  Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health
Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health  Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year
Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year  Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities
Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities  Women in Waste Management: Asia’s Circularity Runs on Women. Its Policies Still Don’t
Women in Waste Management: Asia’s Circularity Runs on Women. Its Policies Still Don’t  Embracing the Business Value of Sustainability
Embracing the Business Value of Sustainability