Ensuring Sustainable Wheat Farming for Global Corporation
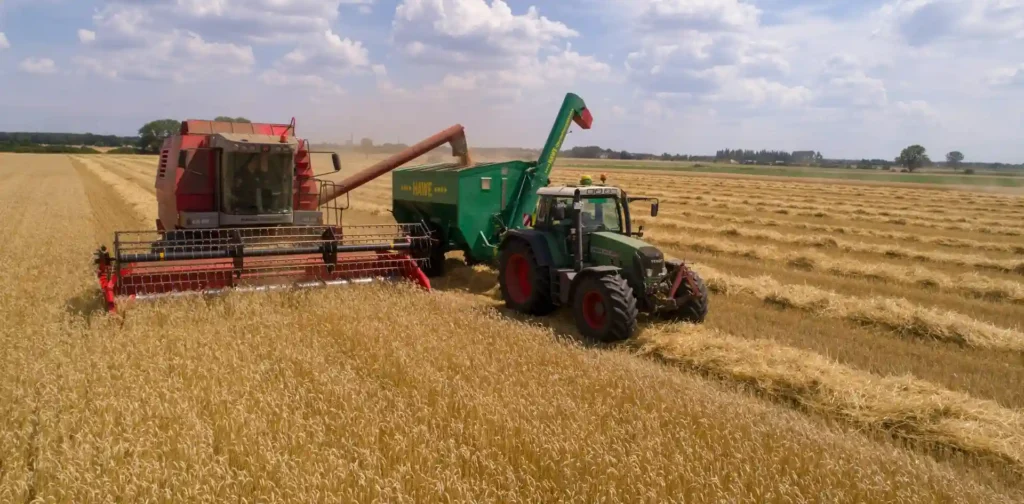

Photo: Heiko Janowski on Unsplash
The expansion of industries driven by increasing market demand has led to significant environmental damage. In the food production sector, large companies have played a role in massive agricultural expansion to meet the supply of food ingredients. Therefore, it is crucial for major companies that depend on the agricultural sector to create sustainable and responsible production methods, such as through mainstreaming regenerative wheat farming.
The Cost of Wheat Production
The agriculture sector both contributes to and is affected by climate change. It accounts for 11% of global greenhouse gas emissions. High-demand agricultural products like wheat, soybeans, and dairy require constant resources and continual expansion.
Wheat is used to make various products such as noodles, biscuits, and bread. It also serves as a staple food in many parts of the world. Wheat cultivation occupies the largest land mass among agricultural plantations, covering about 220 million hectares globally, nearly the size of Greenland.
Beyond the shift in land usage, wheat farming has other significant environmental costs. Research indicates that the largest environmental cost of a loaf of bread comes from fertilizer use in wheat farming. These fertilizers, which contain nitrogen and phosphorus, can leak into the environment if overused. When these fertilizers enter waterways, they can contaminate water sources, harm human health, and cause excessive algae growth, leading to dead zones in aquatic ecosystems.
Regenerative Wheat Farming
To achieve more sustainable agricultural practices, programs that help suppliers minimize environmental damage and enhance sustainability are needed. Regenerative agricultural practices in wheat farming aim to minimize harm from agricultural practices and create a more sustainable production chain. One example is the regenerative agriculture program by Grupo Bimbo, a global food company based in Mexico that produces various wheat-based products.
To implement it, the company developed a project with strategies discussed with agricultural farmer suppliers. Then, farmers were trained through a farmers’ network to achieve environmental goals that promote food system resilience. Essentially, the company provides knowledge to supplier farmers to implement regenerative agriculture programs.
These practices, along with mutual agreements among farmers, have enrolled more than 170,000 hectares of land in the regenerative agriculture program. They have lessened land degradation and aim to create a more sustainable agricultural production system by emphasizing responsibility and transparency.
Corporate Responsibility in Reducing Environmental Damage
Global corporations have a significant responsibility to minimize environmental damage caused by their mass production practices. Therefore, programs that emphasize sustainability and environmental protection are essential. Replicating such programs, tailored to the challenges and needs of different crops or in various regions, can help mitigate the damage caused by large-scale agricultural production.Besides that, government support is also crucial. Governments can promote sustainable farming programs by ensuring supportive policies and resources. Farmers, governments, corporations, and other stakeholders can work together to create more sustainable agricultural practices and strengthen the food system.
Editor: Kresentia Madina


 Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon
Congo Basin Peatlands Are Releasing Ancient Carbon  From Anxiety to Action: How Youth Climate Activism Is Evolving
From Anxiety to Action: How Youth Climate Activism Is Evolving  India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights
India’s Supreme Court Declared Menstrual Health and Hygiene as Fundamental Rights  Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health
Impacts of E-waste Pollution on Animals and Human Health  Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year
Africa’s Solar Energy Surge: Why 2025 Was a Breakthrough Year  Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities
Agrihoods: Integrating Farms and Urban Neighborhoods into Sustainable Communities